Protecting the Web of Life
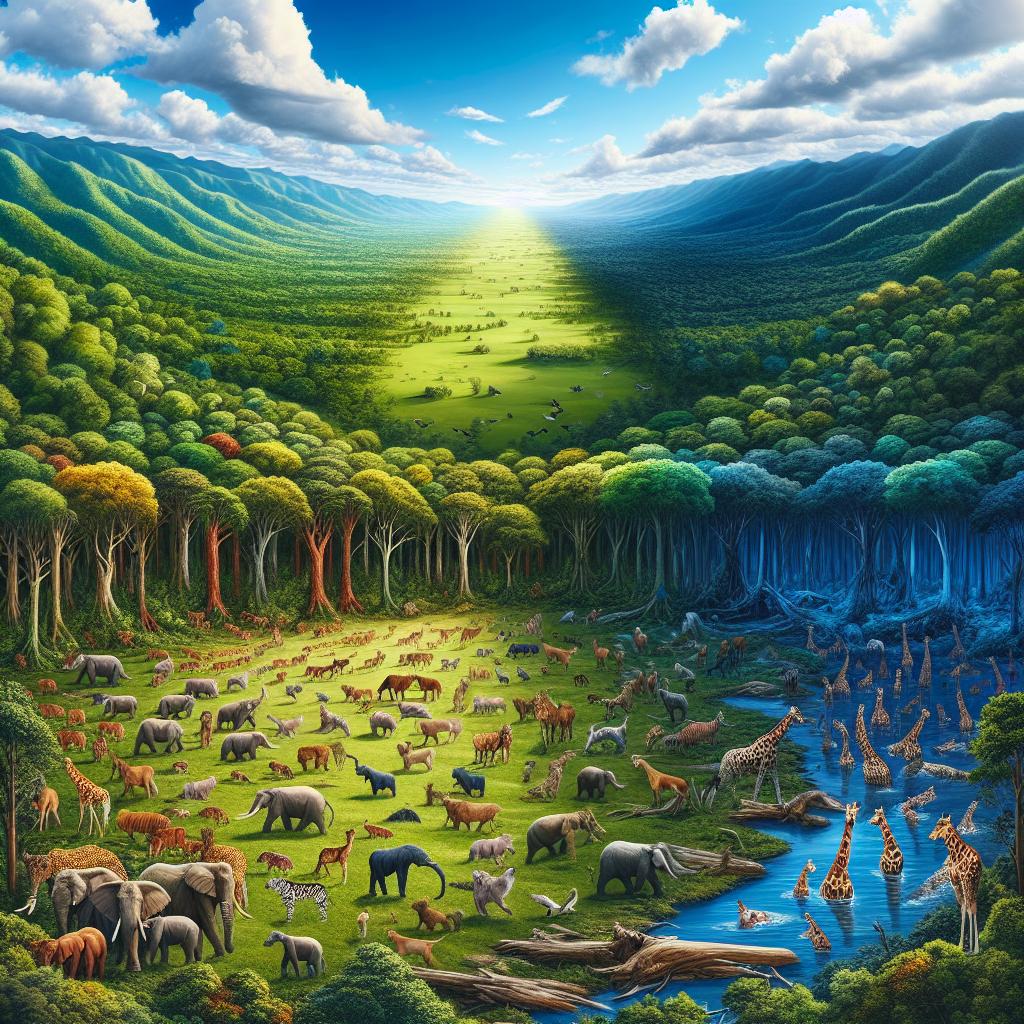

In the intricately connected web of our planet, every element plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. From the tiniest microorganisms to the largest mammals, each species contributes to the intricate web of life that sustains us all. However, this delicate balance is under threat due to various human activities, most notably deforestation. This article explores the importance of biodiversity conservation, wildlife protection, sustainability, and climate justice in the fight against deforestation.
Biodiversity, the variety of life on Earth, is essential for our planet's health and ours. It provides us with food, medicine, clean air, and water. However, according to the latest report by the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), more than one million species are at risk of extinction. Deforestation is a significant driver of this biodiversity loss, as it destroys habitats, fragmenting landscapes and driving many species to the brink of extinction.
Wildlife conservation is closely linked to biodiversity conservation, as wildlife is a key component of biodiversity. Forests are home to more than 80% of the world's terrestrial species, and deforestation threatens their very existence. The loss of wildlife not only has ecological consequences but also economic and social ones. For instance, the tourism industry relies heavily on wildlife, and the loss of iconic species like elephants, tigers, and gorillas can have devastating impacts on local economies.
Sustainability is another critical aspect of the equation. Deforestation is unsustainable, as it leads to long-term consequences such as soil erosion, loss of fertility, and increased greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable forest management, on the other hand, can help mitigate these impacts while providing benefits such as timber, non-timber forest products, and carbon sequestration.
Deforestation is not only an environmental issue but also a social one, with disproportionate impacts on marginalized communities. Indigenous peoples and local communities are often the most affected, as they depend on forests for their livelihoods and cultural practices. Moreover, deforestation can lead to conflicts over land, displacement, and human rights abuses.
Climate justice is another crucial aspect of the equation. Deforestation is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for around 15% of global emissions. The emissions from deforestation disproportionately affect vulnerable communities, who often have the least responsibility for the problem. Climate justice requires that these communities are not only protected from the impacts of deforestation but also have the means to adapt and mitigate its effects.
The good news is that there are solutions. Reforestation and sustainable forest management can help mitigate the impacts of deforestation while providing economic and social benefits. For instance, agroforestry, which involves growing trees alongside crops, can help increase yields, improve soil health, and provide income for farmers. Community-led forest conservation initiatives can help protect forests while providing livelihoods for local communities.
Governments and international organizations also have a critical role to play. Strong legislation and enforcement are necessary to prevent illegal deforestation and promote sustainable forest management. International cooperation and funding are essential to support these efforts and ensure that vulnerable communities are not left behind.
In conclusion, the fight against deforestation requires a holistic approach that addresses biodiversity conservation, wildlife protection, sustainability, and climate justice. The consequences of deforestation are far-reaching and affect us all, from the loss of iconic species to the impacts on vulnerable communities and the global climate. By working together, we can protect the web of life and ensure a sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.