Plowing a Greener Future
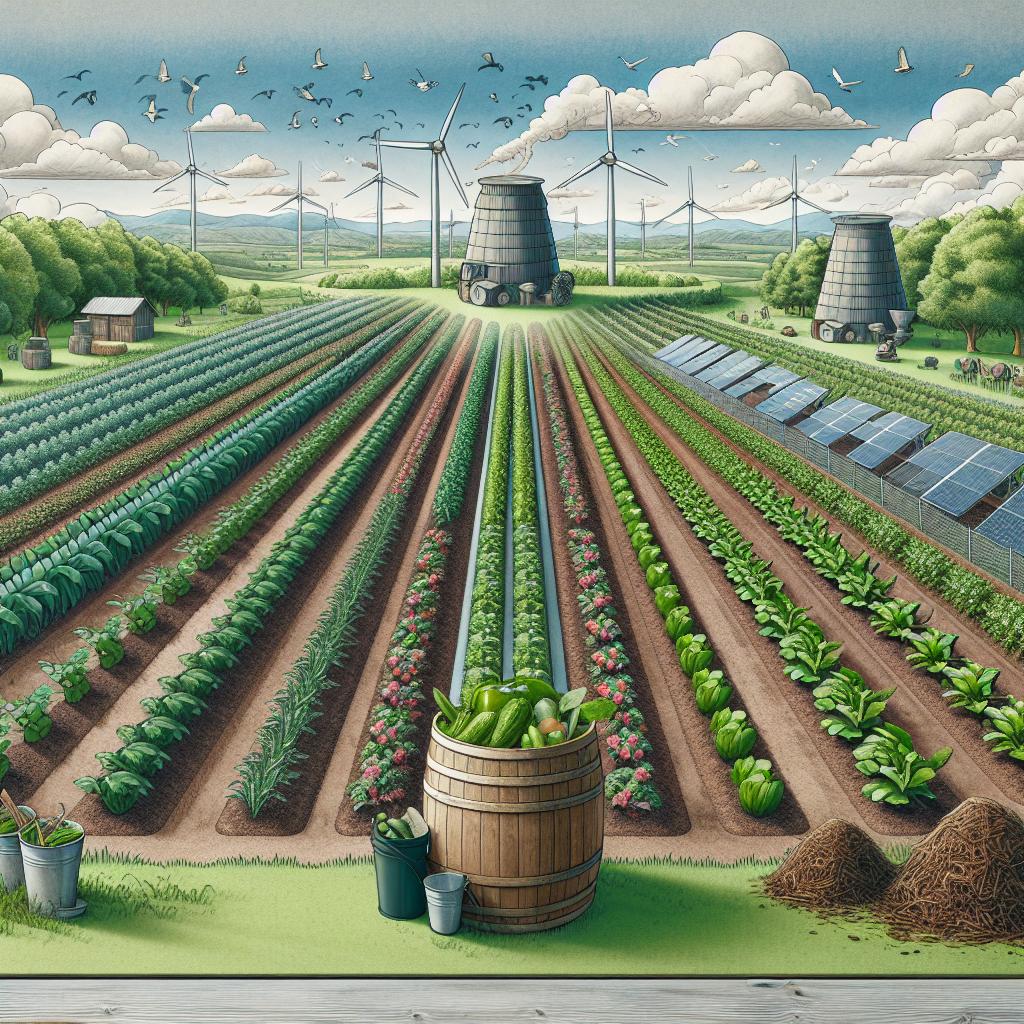

In the face of a rapidly changing climate and increasing global population, the need for sustainable agriculture has never been more pressing. This agricultural approach, which focuses on reducing environmental impact and improving social and economic sustainability, is gaining traction around the world. At the heart of sustainable agriculture lies the integration of green technology, eco-friendly practices, and climate-smart agriculture.
Sustainable agriculture is a holistic farming system that considers the long-term health of the land, the welfare of farmers, and the needs of consumers. This approach stands in contrast to conventional agriculture, which often relies heavily on synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and monoculture farming practices. Sustainable agriculture, on the other hand, emphasizes crop rotation, natural fertilization, and the preservation of natural habitats.
One of the key components of sustainable agriculture is green technology. Green technology refers to the use of renewable resources, energy-efficient processes, and innovative solutions to minimize the environmental impact of agricultural practices. For instance, solar-powered irrigation systems can help farmers conserve water and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. Similarly, precision agriculture using drones and satellite imagery can help farmers optimize their use of fertilizers and reduce agricultural runoff.
Another critical aspect of sustainable agriculture is eco-friendly practices. These practices include reducing the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, implementing integrated pest management systems, and using natural fertilizers such as compost and manure. Additionally, the adoption of agroforestry systems, which combine farming with the cultivation of trees, can help sequester carbon, provide shade, and promote biodiversity.
Climate-smart agriculture is another approach that is gaining popularity in the context of sustainable agriculture. Climate-smart agriculture refers to farming practices that help build resilience to climate change, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and improve food production in the face of a changing climate. For example, the use of drought-resistant crops, conservation agriculture practices, and the adoption of renewable energy sources for agricultural operations can all contribute to climate-smart agriculture.
Soil protection is an essential component of sustainable agriculture. Soil is a non-renewable resource, and its degradation can have significant consequences for agricultural productivity, water quality, and food security. Sustainable agriculture practices, such as no-till farming, crop rotation, and the use of cover crops, can help protect soil health and reduce erosion. Additionally, the adoption of regenerative agriculture practices, which focus on enhancing soil health through the addition of organic matter and the promotion of biodiversity, can help build resilient soils that are better able to withstand the impacts of climate change.
In conclusion, the integration of sustainable agriculture, green technology, eco-friendly practices, climate-smart agriculture, and soil protection offers a promising path forward for meeting the food needs of a growing population while reducing the environmental impact of agricultural practices. These approaches can help build resilient agricultural systems that are better able to withstand the challenges of a changing climate, while also promoting social and economic sustainability. By investing in these practices and technologies, we can create a greener, more sustainable future for agriculture and for the planet.